1. Overview and problem statement
Did you know…?
Germany could cover its entire energy needs from renewable sources and even expand energy use while protecting the climate and environment?12
There is no concert or show without electricity; therefore, the topic is of central importance for events and carries even more significance in times of energy crisis, increasing costs and the urgent need to stop air pollution.
To lower costs, event organizers strive to use energy sources as efficiently as possible. At the same time, artistic visions or musical requirements are not always based on energy consumption, which is in turn dependent on local conditions.
The present challenge for the event industry is that, despite the ongoing energy transition, renewable energies are often still more expensive than “conventional” electricity or harmful fuels such as diesel and gasoline. 13 For open air events, an onsite renewable energy infrastructure is the absolute exception. Presently the German festival industry produces annual emissions from approximately 400 million liter diesel.14
This shows: For event organizers and bands, energy transformation is a key factor in achieving climate-positive events and requires, first and foremost, examining renewable energy sources, in addition to efficiency adjustments.15



2. Our Benchmark for Tempelhof Lab
In order to implement the concerts in the most possible climate positive manner possible, we have set the following goals at Tempelhof Lab:
- Use renewable electricity from the grid in the form of authentic green energy, where the provider invests the earnings from the sale of renewable energy into the expansion of solar panels or wind energy.
- Measure energy consumption and identify potential to increase efficiency.
- Battery storage solutions, designed to be as circular as possible/equipped with battery passports and charged using renewable energies, e.g. solar/PV, wind turbines or green hydrogen.
- Use generators when there are no other options and fill with HVO– or other sustainable fuels 16.
- Communicate with all involved industries and workers onsite to raise awareness of energy efficiency. Communicate measures taken internally (partners and onsite workers) and externally (audience).
3. What worked well, what can be improved?
At Tempelhof Lab, we took various measures to use energy in a sustainable and circular manner.
What worked well?
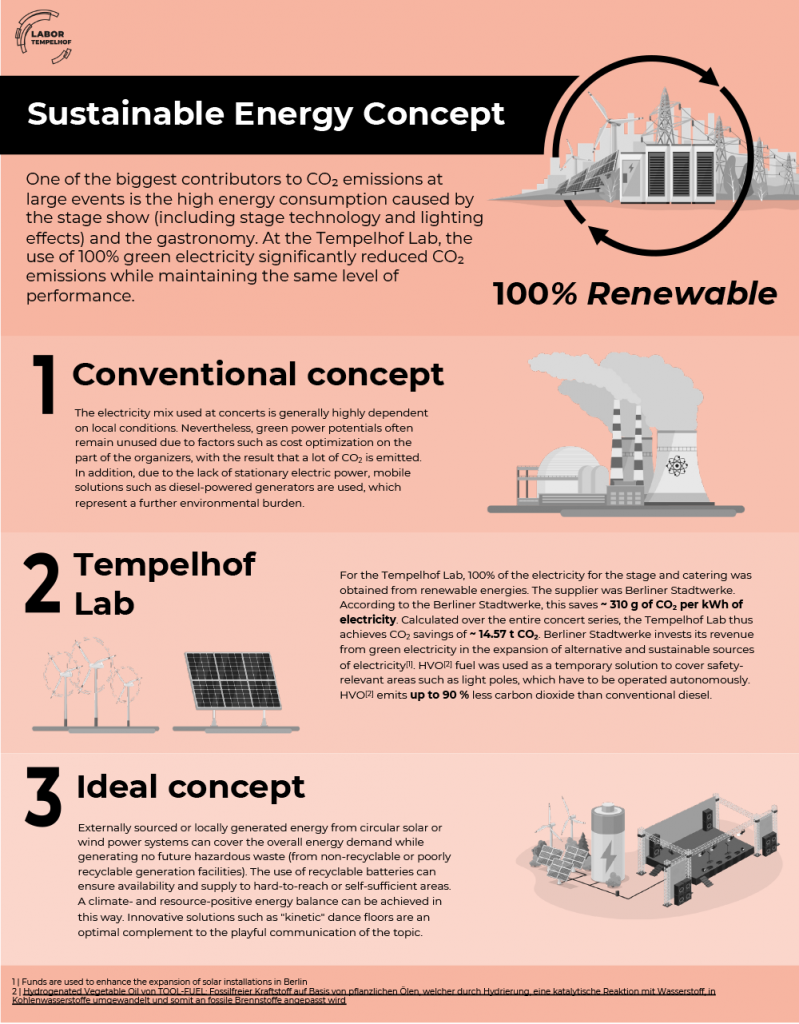
- Entire event site, including the production and food vendor areas, supplied with electricity from the grid (powered with green energy sources). Exceptions were safety-related sources (safety or emergency lighting), which under regulation had to be supplied with an independent power source, and light poles, where the power supply from the grid did not meet the requirements of cable routes of up to 1.5 kilometers.
- 100% elimination of propane gas use by catering and food vendors.
- Use of HVO for light poles and the emergency generator, with 70-90% less CO₂ emissions than diesel.
- Use of solar-powered cell phone charging trees for the public.
What can be improved?
- The procurement of HVO is currently very time- and cost intensive, because the fuel is not widely available (in case of Tempelhof Lab: no provider in Berlin). Germany currently lacks a nationwide delivery system. Germany currently lacks a nationwide delivery system.
- Use other renewable energy sources, such as long-term energy storage, photovoltaic systems, etc.
- Create an accurate energy plan and measure how much electricity is consumed in which areas. Based on this, develop further energy saving measures and efficiencies.
- Ideal energy storage solutions based on recyclable batteries are not yet available on the market today. However, this structural problem is slated to be addressed at the political level by the EU Battery Regulation, so that such solutions are available in the coming years.



4. Findings and Recommendations
- Switching to renewable energies is the single biggest factor in reducing an event’s carbon footprint. By switching from diesel generators to green electricity from the grid, we were able to reduce CO₂ emissions in the area of energy electricity by 95% 17. Therefore all event organizers should focus on energy sources at the earliest stages of planning.
- For fixed locations, it is advisable to switch to authentic green electricity through an appropriate supplier.
- If the location is secure and will be used for several years (e.g. open-air festivals), the installation of a renewable power grid can be a sensible medium-term investment. Public subsidies 18 may be available.
- In the case of a one-off event, an attempt should be made to enter into discussions with the site owner and energy company to develop solutions together. The temporary relocation of fixed power, as with Tempelhof Lab, means additional costs for a one-time use, both in terms of technical implementation and material as well as personnel planning.
- Due to many possible variations in site conditions, all energy sources should be considered individually during planning.
- If the purchase of green electricity is not possible due to local dependencies on a particular supplier, there are offsets to compensate for this energy consumption and the associated emissions. However, all other options should be examined beforehand.
- The conversion to electricity from the grid means considerable additional expense due to the relocation of the corresponding infrastructure across the entire site (transformer stations, laying of several kilometers of cable bridges, scaffolding bridges, etc.).
- In addition, the switch to fixed current can have an impact on individual industries. For example, in the catering industry: a deep fryer heats up faster with gas than with electricity.
- Inform vendors and contractors in advance about alternative energy measures and solicit feedback on possible needs and requirements. If this is done at an early stage, organizers and contractors can find solutions together.
- Alternative fuels such as HVO are a good solution where fuel is absolutely necessary. However, it is currently very costly due to low supply.
- Closely monitor supply trends in the market.
- For locations near HVO producers, procurement is easier and delivery distances are shorter.
- Green hydrogen: Hydrogen may be an alternative to HVO in some locations and regions. This depends on how much energy is lost in production (how much energy is needed to produce a given amount of hydrogen).
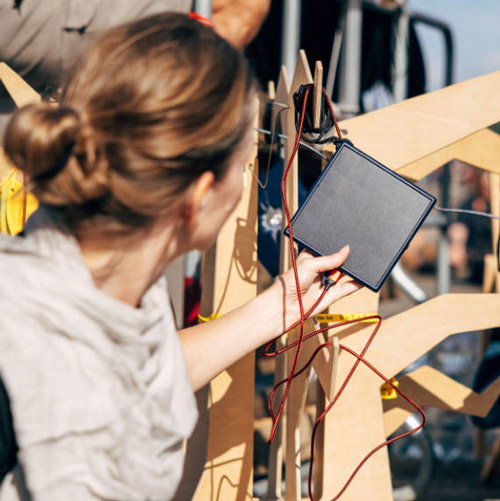
- Projects like solar trees as mobile phone charging stations, although not the most important factor for shrinking an event’s carbon footprint, have a very big educational effect, as discussions with the public showed at Tempelhof Lab. This is true for projects where the public can actively participate, for example, by riding stationary bikes or dancing on floor panels to generate kinetic energy.
- Projects of this kind should be taken into account in advance during the planning stage and appropriate space should be made available.
- If such projects cannot be carried out by the organizers themselves: Bring NGOs and associations on board to strengthen the educational effect by offering informative materials and interactive volunteers onsite.
- The use of batteries as a storage solution – for example, for light poles or point-of-sale systems – requires a long planning period, as their capacity is limited and different potentials have to be considered, including:
- Connection to fixed power/electricity.
- Alternative: for battery solutions, enter into early discussion with power service provider.
- Alternative: Use HVO fuel-powered generators instead of diesel.
- Even when using renewable energy, it is best to use energy as efficiently as possible.
- Accurately record power usage including peaks to control the energy supply well and, if necessary, balance it through peak shaving and/or smart grids.
5. Service Provider Contacts



6. Further inspiration from the industry
The Futur2 Festival (capacity 5,000) in Hamburg designs and scales their festival only as large as it can be powered by renewable energy. A solar array provides energy for the existing battery storage, and the stage is powered by energy generated from generators on stationary bicycles. The pedal resistance increases with the energy demand on stage, making energy tangible and understandable. When the bass kicks in and the lights come on, it becomes harder to pedal. 19 Even Coldplay tackled renewable energy during their 2022 world tour. By having the audience dance on kinetic floor plates, the energy the dancing generated was stored in batteries, making it possible for the audience to see how energy is created.20 However, this merely served as an educational opportunity and not as an important part of the concert’s energy supply.
The Shambala festival (capacity 25,000) in Great Britain focuses on two major themes: renewable energies (access to the power grid, solar energy, biofuels, batteries and bio-fluid gas) and reducing energy use by monitoring consumption. Between 2010 and 2019, Shambala reduced onsite emissions by 90%, as well as the number of generators used, from 26 to 15 in three years – despite growing audience numbers. The festival claims to have no additional costs for sustainability measures based on blended costing, i.e., saving fuel saves money. 21